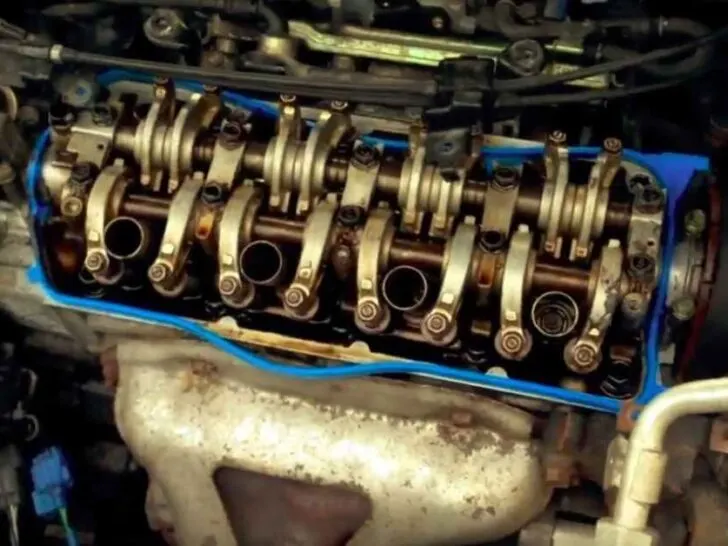
D17A1 and D17A2 are the engine options for the 7th generation Honda Civic from the 2001-2005 models. Both have the same 1.7-liter displacement and other matching features, including mechanical construction, the number of cylinders, and physical dimensions.
What is the Difference Between D17A1 and D17A2? The primary difference between the D17A1 and D17A2 engines is that the latter has a VTEC system. In addition, D17A1 has a compression ratio of 9.5:1 while the other engine has 9.9:1 due to differences in piston design. Other differences are in cylinder heads, oil pan, and exhaust system. D17A1 is an engine option for 2001-2005 model LX/DX trims, while the other is part of EX/HX trim levels of Honda Civic. Furthermore, you can swap both engines with a few modifications to cater to the VTEC, exhaust system, and O2 sensors in D17A2.
This article will guide Honda Civic owners in comparing 1.7-liter A1 and A2 engines. We will also discuss the reliability, interchangeability of parts, and compatibility of both engines with performance-boosting hardware like turbochargers.
Specifications of D17A1
It belongs to the D17A group of D-series engines by Honda motor company. It has a 1.7-liter displacement that is larger than previous D16 generations.
Therefore, it has better power and torque ratings. It has a cylinder block made of aluminum with 4 cylinders in an Inline configuration.
Furthermore, it has a Single Overhead Camshaft (SOHC) valve train with 4 valves per cylinder.
It has a compression ratio of 9.5:1 due to dished piston heads with no quench pads. It has a maximum speed of 6700-6800 rpm.
Moreover, it is compatible with gasoline fuel and has good fuel economy even for used engines.
You should change its oil for a 2900-5800 miles interval depending on the conventional or synthetic oil type for longevity in its life. It is available in 2001-2005 Honda Civic DX/LX trim levels.
Specifications of D17A2
D17A2 is a 1.7-liter I4 engine with 16 valves for 4 cylinders. It has an aluminum cylinder head with a modified design to work with the VTEC system developed by Honda.
VTEC differs from conventional variable valve timing systems and uses a different camshaft profile according to its revolutions per minute (RPM).
The exhaust system has upgraded parts like a catalytic converter, Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve, and O2 sensors to work with the VTEC system.
In addition, its pistons have small quench pads giving it a higher compression ratio of 9.9:1. It is a part of the 2001-2005 Honda Civic EX/HX premium trim levels.
List of Differences between D17A1 and D17A2 engines
D17A1 and D17A2 belong to the D-series of Inline 4-cylinder engines used in cars like the Honda Civic.
Both have the same similarities and differences because both remained in service in parallel from 2001-2005 in Honda vehicles for the US market.
Here is a comparison of different systems and features of both engines to give a clear picture of their significant differences:
Power rating
Honda D17A1 has a power rating of 121-123 hp at 6300-6400 rpm. However, D17A2 can deliver 126-128 hp, about 5 hp more than the first.
In addition, the power boost has improved head design, advanced valve timing control, and a high compression ratio.
Therefore, in this category, D17A2 clearly has the edge over the other and can be the choice of car owners while buying a used one.
Torque rating
The torque rating is not much of a concern for customers when buying passenger cars like Honda Civic.
However, there is a minimum requirement to pull the specified load of the vehicle.
D17A1 has a torque rating of 108-112 lb-ft, varying according to the engine rpm.
This specification is at 4490-4510 rpm. In comparison, D17A2 has slightly better torque specifications of 113-115 hp rated at 4790-4810 rpm.
Valve train
Both have the same types of valve and single overhead camshaft (SOHC) design.
Moreover, each has 4 valves per cylinder and a total of 16 valves. However, their main difference is the presence of variable valve timing and lift electronic control (VTEC) in D17A2, which the other engine lacks.
It uses separate camshaft profiles for high and low speeds to improve its performance and fuel efficiency.
At higher rpm, the camshaft opens up the valves more for more air to fuel mixture to improve power.
While at lower rpm below 2300-3200, it switches the camshaft such that valves are less open to improving fuel consumption.
Due to VTEC, both engines also have different camshaft profiles, and D17A2 is better in this aspect due to this new technology resulting in better performance at high rpm and fuel saving at low rpm.
Applications
Both engines have the same applications as far as model years and vehicles are concerned.
D17A1 is available in the base trim level of Honda Civic that is EX for the 2001-2005 model years.
While the other engine is an option for the premium version of Honda Civic EX for the US market for 2001-2005 models. You will also find it in the same car for other markets like Canada, Europe, and Japan.
Compatible transmission system
You can notice a difference in gear ratios of both engines. D17A2 has shorter gears for a 5-speed manual from 3.143 to 0.757 for 5 forward gears and a reverse one.
While the other has ratios from 3.462 to 0.71. The same is true for the 4-speed automatic.
Both are compatible with 4-speed automatic and 5-speed manual transmission and have the same bell housing bolt pattern.
Gas mileage
D17A2 has better gas mileage with VTEC technology. Different camshaft profiles according to low and high rpm result in efficient valve opening according to power requirements.
Therefore, it has a combined fuel economy of more than 30 mpg.
On the other hand, D17A1 also has reasonable combined highway and city areas mpg figures in the range of 27-29 for the used engine.
However, it is less fuel efficient than the first option. Both designs have higher airflow intake ports to improve fuel economy than previous D-series variants.
ECU
D17A2 is a VTEC engine, while A1 lacks this feature. At the same time, ECU has a significant role in activating this upgraded technology to improve its efficiency and performance.
Therefore, they have different wiring harnesses and O2 sensors. However, other programming functions are similar in both of these.
Therefore, there is a space for swapping the ECU between them with minor modifications.
For example, with a digital airflow controller (AFC2), you can use the A2 ECU on A1 without changing wiring harnesses with benefits like better air-fuel mixture and provision of VTEC signal.
Oil pan
D17A2 engines in EX and HX trims of Honda Civic have aluminum oil pans.
While the D17A1 engine in DX/LX trims has a steel pan. Both also have different studs for their mounting on the machine.
Another difference is D17A2 engine has more capacity for engine oil because it requires extra oil to fulfill the requirements of the VTEC head, involving more mechanical interactions. Furthermore, the drain plug for the oil pan is also different in both engines.
Exhaust system
Both D17A1 and D17A2 have different exhaust components and their placement.
The catalytic converter is at a different place in both. Other exhaust components, including headers and downpipe, differ between EX trim containing D17A2 and LX/DX with A1 engine.
Initially, EGR on D17A2 header in the EX trim level, while for 2004-2005, it became available for all trim levels and both variants.
Sensors
There is a difference in O2 sensors between both engines. EX being premium trim level, has wideband O2 sensors with D17A2 engine.
On the other hand, D17A1 has narrow band sensors for 2001-2003 models. Their difference is related to quality and their position at VTEC head.
Moreover, there is also a difference in the location of the secondary O2 sensor in both engines.
Therefore, you must modify the wiring harness to prevent any error code if you go for a head swap.
Compression ratio
Honda D17A1 has a compression ratio of 9.5:1, while D17A2 has 9.9:1. The quotient is higher for the second engine due to differences in its piston design.
It has quench pads on piston heads to provide more compression compared to the dish head design in the other motor. Higher compression gives a higher power rating to the D17A2.
However, the 2nd engine variant has the possibility of gaining better performance while installing it with a turbocharger to compress air.
Physical dimensions
There are a lot of similarities and a few differences in physical dimensions and relevant parameters, including displacement, bore size, stroke length, and rod length.
Both have the same displacement of 1668cc (1.7-liter), the same bore of 2.94 inches (75mm), and the stroke length of 3.72 inches (94.4mm).
Moreover, they also have the same cylinder block but different heads to cater for VTEC in D17A2 and differences in the camshaft profile.
Furthermore, the A2 head will bolt onto the A1 block without issues. They also have the same mounting bolt positions and stud dimensions.
Can you swap the parts between D17A1 and D17A2?
Both are mechanically the same having the same displacement, bore, and stroke size with few differences like VTEC head, exhaust system, ECU, and piston design.
Therefore, you can interchange the parts between them. Some components are bolt-on replacements, while others require modification to make them work.
You can also completely swap a non-VTEC engine with VTEC D17A2 with no change for mechanical parts.
However, if you want to activate the VTEC option, you have to buy AFC2. Otherwise, you must reprogram the ECU, change the wiring harness, and relocate the O2 sensors.
Exhaust system components like header, downpipes, and catalytic converter also are different and need a complete replacement for the engine swap.
Reliability of D17A1 VS D17A2
Both are highly reliable, and people prefer the 2001-2005 model Honda Civics because of their excellent track record regarding reliability.
On the other hand, people are confused about the VTEC system on the D17A2 engine as weak points requiring more maintenance due to the variable camshaft profile and its switching at different speeds.
However, according to customer reviews, Honda claims, and experts’ opinions, there are no issues associated with this variable valve timing system.
Therefore, they can run without problems for 300,000-350,000 miles through regular maintenance with the replacement of minor parts like bearings, gaskets, rings, timing belts, and washers.
At the same time, D17A1 has a simple construction with less complicated features like a camshaft in the absence of variable valve timing. Therefore, it has compatible or better reliability than the A2 variants of D17.
Which is better for turbo installation, D17A1 or D17A2?
Both of these are naturally aspirated without any power-boosting hardware like a turbo or supercharger.
However, there are turbo kits available compatible with both machines. The first one has a low compression ratio; therefore, it has a broader scope for installing a turbocharger to compress the air for a power boost.
You can also use it with D17A2, but pressure should not increase beyond the acceptable range; otherwise, it can damage its parts.
The maximum power limit is 198-202 hp, as going beyond it is unsafe with stock hardware.
However, an expensive proposition is to use low compression pistons, and you can achieve higher air pressures for a power boost above 202 hp.
Related Articles: